本文列举了简单的数值方法:Euler 方法、后退 Euler 方法、梯形公式、改进 Euler 方法,并用 MATLAB 求解线性 ODE,最后展示了输出结果。
常微分方程初值问题
考虑 常微分方程初值问题,设
通常
线性 ODE 例子
方程的真解:
Euler 方法
Euler 方法数值求解
MATLAB 程序1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23% Euler1.m
% Euler method for the ODE model
% u'(x)=x^2+x-u, x in [0,1]
% Initial condition: u(0)=0 ;
% Exact solution: u(x)=-exp(-x)+x^2-x+1.
clear all; close all;
h=0.1;
x=0:h:1; % interval partition
N=length(x)-1;
u(1)=0; % initial value
fun=@(t,u) t.^2+t-u; % RHS
for n=1:N
u(n+1)=u(n)+h.*fun(x(n),u(n));
end
ue=-exp(-x)+x.^2-x+1; % exact solution
plot(x,ue,'b-',x,u,'r+','LineWidth',1)
legend('Exact','Numerical','location','northwest')
% title('Euler method','fontsize',12)
set(gca,'fontsize',12)
xlabel('x','fontsize',16), ylabel('u','fontsize',16)
% print -dpng -r600 Euler1.png
% print -depsc2 Euler1.eps
输出结果
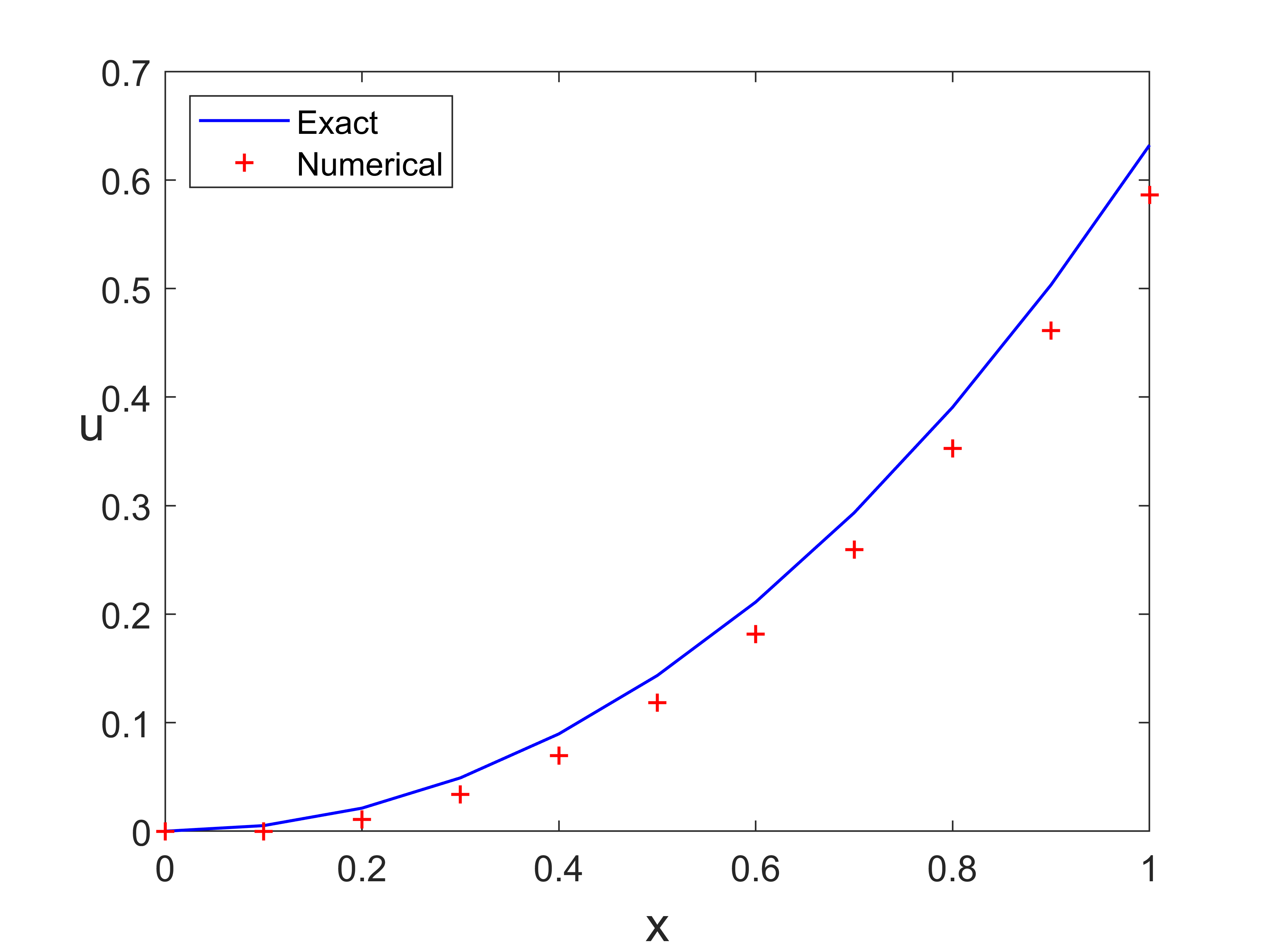
后退 Euler 方法
梯形公式
梯形公式数值求解
梯形公式与后退 Euler 方法类似,这里考虑梯形公式,对于线性 ODE 例子:
可得
MATLAB 程序
1 | % Trapezoidal.m |
输出结果
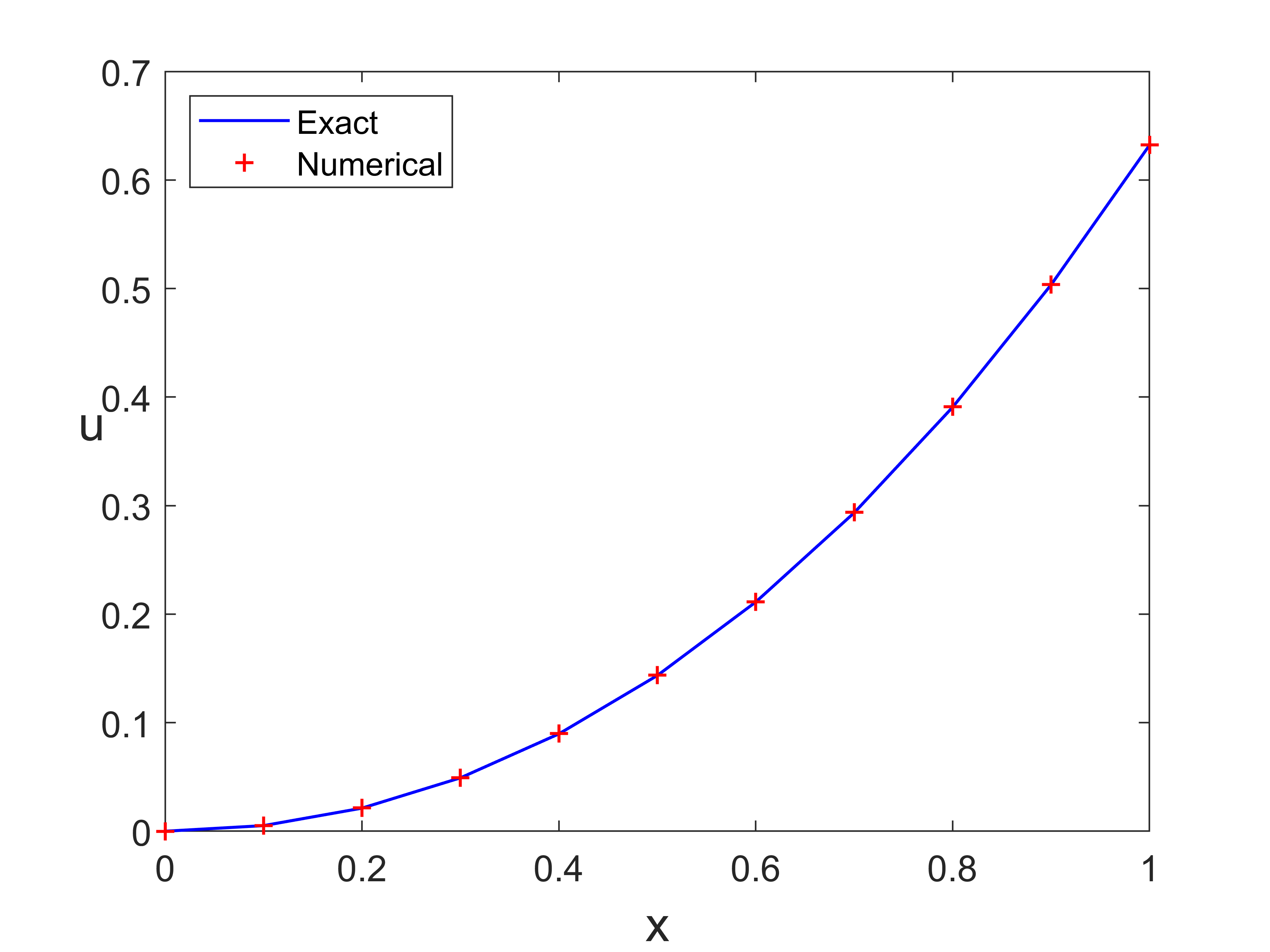
改进的 Euler 方法
预估校正
MATLAB 程序
1 | % ModiEuler.m |
输出结果
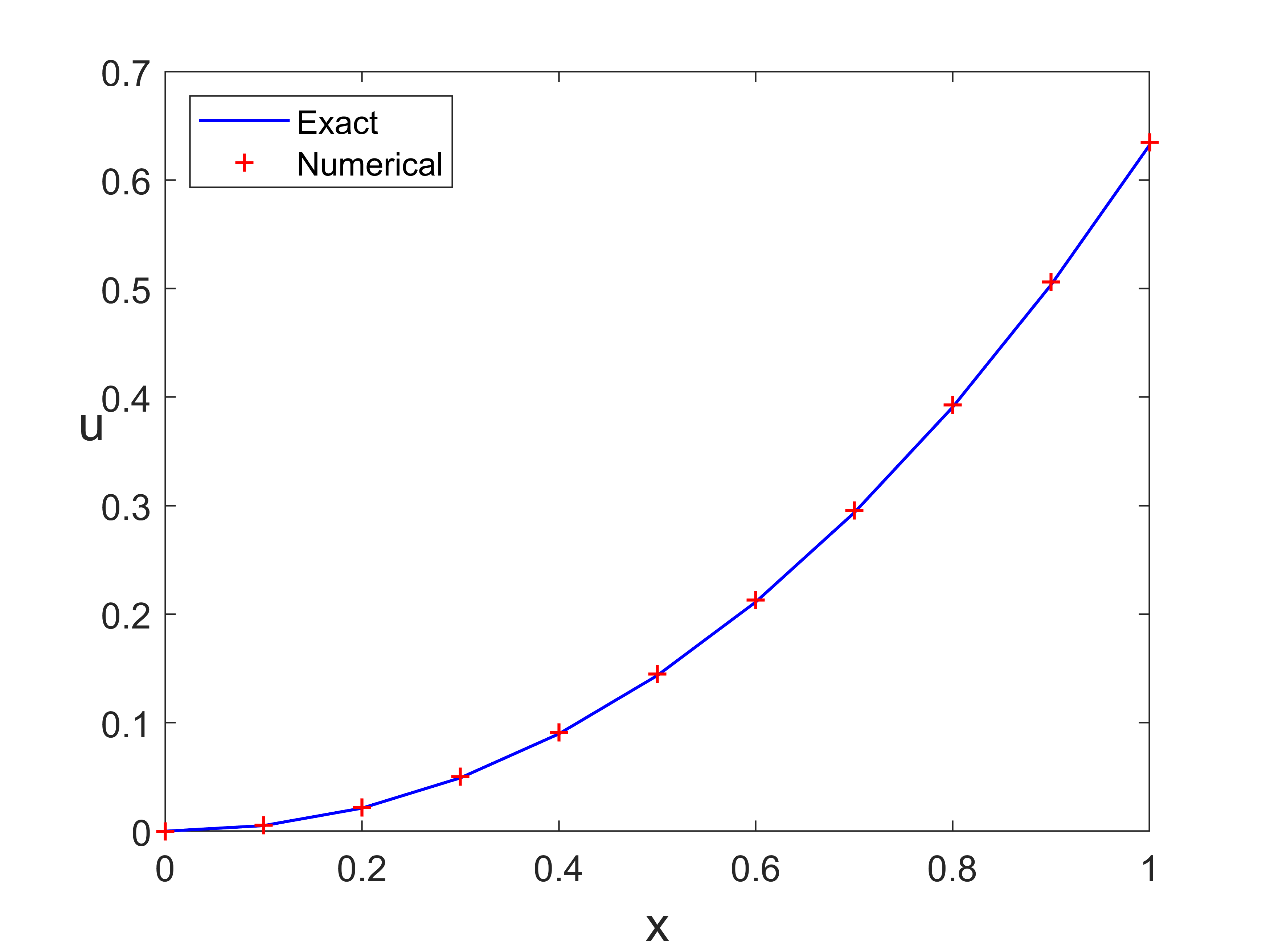
参考书籍
- 数值分析 第 5 版 (李庆扬等)
- MATLAB 微分方程高效解法